import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.dates import DateFormatter
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
import warnings
# Suppress FutureWarnings
warnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=FutureWarning)
warnings.simplefilter(action='ignore', category=UserWarning)
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(style="ticks", font_scale=1.5) # white graphs, with large and legible letters
# %matplotlib widget22 challenge
22.1 Importing Bad .csv Files
Here we will get a taste of what it feels like to work with bad .csv files and how to fix them.
TO DO:
- Create a folder for this challenge, name it whatever you want.
- Download this Jupyter notebook and move it to that folder.
- Download these 3
.csvfiles and part 2 notebook:- cleaning1
- cleaning2-
- cleaning3
- Go to
challenge part 2and download it from there.
- Move these files into your folder.
22.1.1 Import
22.2 dataset 1
| date | A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2023-01-01 00:00:00 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 1 | 2023-01-01 00:05:00 | 1 | 2.245251 | -1.757193 | 1.899602 | -0.999300 |
| 2 | 2023-01-01 00:10:00 | 2 | 2.909648 | 0.854732 | 2.050146 | -0.559504 |
| 3 | 2023-01-01 00:15:00 | 3 | 3.483155 | 0.946937 | 1.921080 | -0.402084 |
| 4 | 2023-01-01 00:20:00 | 2 | 4.909169 | 0.462239 | 1.368470 | -0.698579 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 105115 | 2023-12-31 23:35:00 | -37 | 1040.909898 | -14808.285199 | 1505.020266 | 423.595984 |
| 105116 | 2023-12-31 23:40:00 | -36 | 1040.586547 | -14808.874072 | 1503.915566 | 423.117110 |
| 105117 | 2023-12-31 23:45:00 | -37 | 1042.937417 | -14808.690745 | 1505.479671 | 423.862810 |
| 105118 | 2023-12-31 23:50:00 | -36 | 1042.411572 | -14809.212002 | 1506.174334 | 423.862432 |
| 105119 | 2023-12-31 23:55:00 | -35 | 1043.053520 | -14809.990338 | 1505.767197 | 423.647007 |
105120 rows × 6 columns
Now let’s put the column ‘date’ in the index with datetime format
# we can change the format of the column to datetime and then set it as the index.
df1['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df1['date'])
df1.set_index('date', inplace=True)
df1| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| date | |||||
| 2023-01-01 00:00:00 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2023-01-01 00:05:00 | 1 | 2.245251 | -1.757193 | 1.899602 | -0.999300 |
| 2023-01-01 00:10:00 | 2 | 2.909648 | 0.854732 | 2.050146 | -0.559504 |
| 2023-01-01 00:15:00 | 3 | 3.483155 | 0.946937 | 1.921080 | -0.402084 |
| 2023-01-01 00:20:00 | 2 | 4.909169 | 0.462239 | 1.368470 | -0.698579 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2023-12-31 23:35:00 | -37 | 1040.909898 | -14808.285199 | 1505.020266 | 423.595984 |
| 2023-12-31 23:40:00 | -36 | 1040.586547 | -14808.874072 | 1503.915566 | 423.117110 |
| 2023-12-31 23:45:00 | -37 | 1042.937417 | -14808.690745 | 1505.479671 | 423.862810 |
| 2023-12-31 23:50:00 | -36 | 1042.411572 | -14809.212002 | 1506.174334 | 423.862432 |
| 2023-12-31 23:55:00 | -35 | 1043.053520 | -14809.990338 | 1505.767197 | 423.647007 |
105120 rows × 5 columns
If we know that in advance, we can write everything in one command when we import the csv.
df1 = pd.read_csv('cleaning1.csv',
index_col='date', # set the column date as index
parse_dates=True) # turn to datetime format
df1| A | B | C | D | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| date | |||||
| 2023-01-01 00:00:00 | 0 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2023-01-01 00:05:00 | 1 | 2.245251 | -1.757193 | 1.899602 | -0.999300 |
| 2023-01-01 00:10:00 | 2 | 2.909648 | 0.854732 | 2.050146 | -0.559504 |
| 2023-01-01 00:15:00 | 3 | 3.483155 | 0.946937 | 1.921080 | -0.402084 |
| 2023-01-01 00:20:00 | 2 | 4.909169 | 0.462239 | 1.368470 | -0.698579 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2023-12-31 23:35:00 | -37 | 1040.909898 | -14808.285199 | 1505.020266 | 423.595984 |
| 2023-12-31 23:40:00 | -36 | 1040.586547 | -14808.874072 | 1503.915566 | 423.117110 |
| 2023-12-31 23:45:00 | -37 | 1042.937417 | -14808.690745 | 1505.479671 | 423.862810 |
| 2023-12-31 23:50:00 | -36 | 1042.411572 | -14809.212002 | 1506.174334 | 423.862432 |
| 2023-12-31 23:55:00 | -35 | 1043.053520 | -14809.990338 | 1505.767197 | 423.647007 |
105120 rows × 5 columns
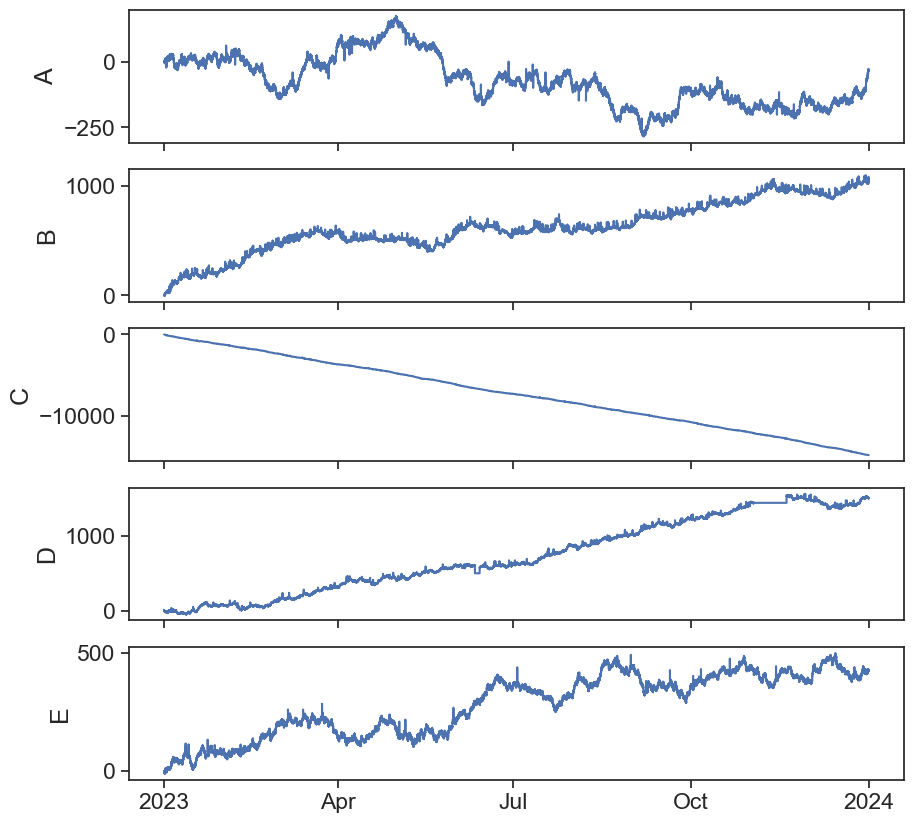
Now let’s plot all the columns and see what we have.
def plot_all_columns(data):
column_list = data.columns
fig, ax = plt.subplots(len(column_list),1, sharex=True, figsize=(10,len(column_list)*2))
if len(column_list) == 1:
ax.plot(data[column_list[0]])
return
for i, column in enumerate(column_list):
ax[i].plot(data[column])
ax[i].set(ylabel=column)
locator = mdates.AutoDateLocator(minticks=3, maxticks=7)
formatter = mdates.ConciseDateFormatter(locator)
ax[i].xaxis.set_major_locator(locator)
ax[i].xaxis.set_major_formatter(formatter)
returnLooks like some of this data needs cleaning…
22.3 dataset 2
| A B date time | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 0.0 01012023 00:00:00 |
| 1 | -2.0275363548598184 0.011984922825112581 01012... |
| 2 | -2.690616715983192 -0.29792822981957684 010120... |
| 3 | -1.9859899758267612 -0.30940867922490206 01012... |
| 4 | -2.290897621584889 -2.8666633353521624 0101202... |
| ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.51464473079395 293.8680858227996 31122023 ... |
| 8756 | -74.73805809332175 294.7593463919649 31122023 ... |
| 8757 | -75.84842465358788 294.07634907736116 31122023... |
| 8758 | -77.27218272637339 293.526461290973 31122023 2... |
| 8759 | -76.55739976945038 293.35336890454107 31122023... |
8760 rows × 1 columns
Something is wrong…
Let’s open the actual .csv file and take a quick look.
It seems that the values are separated by spaces and not by commas ,.
| A | B | date | time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.0 | 1012023 | 00:00:00 |
| 1 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 | 1012023 | 01:00:00 |
| 2 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 | 1012023 | 02:00:00 |
| 3 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 | 1012023 | 03:00:00 |
| 4 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 | 1012023 | 04:00:00 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 | 31122023 | 19:00:00 |
| 8756 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 | 31122023 | 20:00:00 |
| 8757 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 | 31122023 | 21:00:00 |
| 8758 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 | 31122023 | 22:00:00 |
| 8759 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 | 31122023 | 23:00:00 |
8760 rows × 4 columns
# convert the date column to datetime
df2['date_corrected'] = pd.to_datetime(df2['date'])
# df2['date_corrected'] = pd.to_datetime(df2['date'], format='%d%m%Y')
df2| A | B | date | time | date_corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.0 | 1012023 | 00:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.001012023 |
| 1 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 | 1012023 | 01:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.001012023 |
| 2 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 | 1012023 | 02:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.001012023 |
| 3 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 | 1012023 | 03:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.001012023 |
| 4 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 | 1012023 | 04:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.001012023 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 | 31122023 | 19:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.031122023 |
| 8756 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 | 31122023 | 20:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.031122023 |
| 8757 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 | 31122023 | 21:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.031122023 |
| 8758 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 | 31122023 | 22:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.031122023 |
| 8759 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 | 31122023 | 23:00:00 | 1970-01-01 00:00:00.031122023 |
8760 rows × 5 columns
data_types = {'date': str , 'time':str}
# Read the CSV file with specified data types
df2 = pd.read_csv('cleaning2-.csv', delimiter=' ', dtype=data_types)
df2| A | B | date | time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.0 | 01012023 | 00:00:00 |
| 1 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 | 01012023 | 01:00:00 |
| 2 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 | 01012023 | 02:00:00 |
| 3 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 | 01012023 | 03:00:00 |
| 4 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 | 01012023 | 04:00:00 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 | 31122023 | 19:00:00 |
| 8756 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 | 31122023 | 20:00:00 |
| 8757 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 | 31122023 | 21:00:00 |
| 8758 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 | 31122023 | 22:00:00 |
| 8759 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 | 31122023 | 23:00:00 |
8760 rows × 4 columns
| A | B | date | time | date_corrected | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.0 | 01012023 | 00:00:00 | 2023-01-01 |
| 1 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 | 01012023 | 01:00:00 | 2023-01-01 |
| 2 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 | 01012023 | 02:00:00 | 2023-01-01 |
| 3 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 | 01012023 | 03:00:00 | 2023-01-01 |
| 4 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 | 01012023 | 04:00:00 | 2023-01-01 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 | 31122023 | 19:00:00 | 2023-12-31 |
| 8756 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 | 31122023 | 20:00:00 | 2023-12-31 |
| 8757 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 | 31122023 | 21:00:00 | 2023-12-31 |
| 8758 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 | 31122023 | 22:00:00 | 2023-12-31 |
| 8759 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 | 31122023 | 23:00:00 | 2023-12-31 |
8760 rows × 5 columns
| A | B | date | time | date_corrected | datetime | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.0 | 01012023 | 00:00:00 | 2023-01-01 | 2023-01-01 00:00:00 |
| 1 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 | 01012023 | 01:00:00 | 2023-01-01 | 2023-01-01 01:00:00 |
| 2 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 | 01012023 | 02:00:00 | 2023-01-01 | 2023-01-01 02:00:00 |
| 3 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 | 01012023 | 03:00:00 | 2023-01-01 | 2023-01-01 03:00:00 |
| 4 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 | 01012023 | 04:00:00 | 2023-01-01 | 2023-01-01 04:00:00 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 8755 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 | 31122023 | 19:00:00 | 2023-12-31 | 2023-12-31 19:00:00 |
| 8756 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 | 31122023 | 20:00:00 | 2023-12-31 | 2023-12-31 20:00:00 |
| 8757 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 | 31122023 | 21:00:00 | 2023-12-31 | 2023-12-31 21:00:00 |
| 8758 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 | 31122023 | 22:00:00 | 2023-12-31 | 2023-12-31 22:00:00 |
| 8759 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 | 31122023 | 23:00:00 | 2023-12-31 | 2023-12-31 23:00:00 |
8760 rows × 6 columns
df2.drop(columns=['date', 'time', 'date_corrected'], inplace=True)
df2.set_index('datetime', inplace=True)
df2| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| datetime | ||
| 2023-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.000000 | 0.0 |
| 2023-01-01 01:00:00 | -2.027536 | 0.011984922825112581 |
| 2023-01-01 02:00:00 | -2.690617 | -0.29792822981957684 |
| 2023-01-01 03:00:00 | -1.985990 | -0.30940867922490206 |
| 2023-01-01 04:00:00 | -2.290898 | -2.8666633353521624 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 2023-12-31 19:00:00 | -74.514645 | 293.8680858227996 |
| 2023-12-31 20:00:00 | -74.738058 | 294.7593463919649 |
| 2023-12-31 21:00:00 | -75.848425 | 294.07634907736116 |
| 2023-12-31 22:00:00 | -77.272183 | 293.526461290973 |
| 2023-12-31 23:00:00 | -76.557400 | 293.35336890454107 |
8760 rows × 2 columns
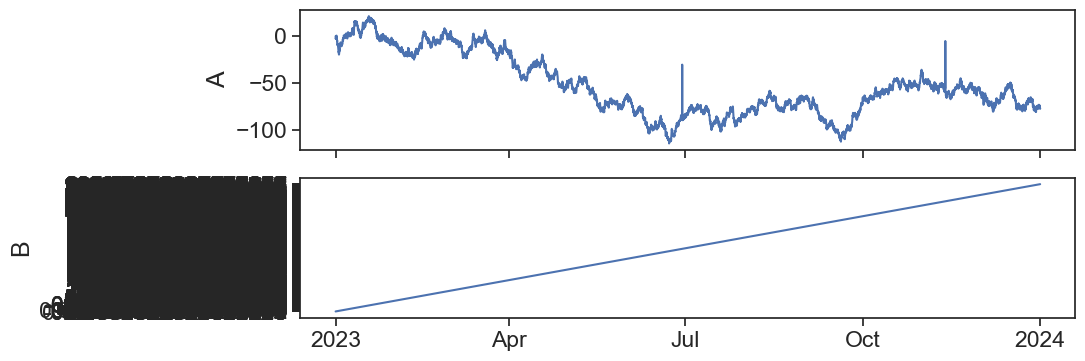
What happened in the second ax?
# use pd.to_numeric to convert column 'B' to float
df2['B'] = pd.to_numeric(df2['B'],
errors='coerce' # 'coerce' will convert non-numeric values to NaN if they can't be converted
)
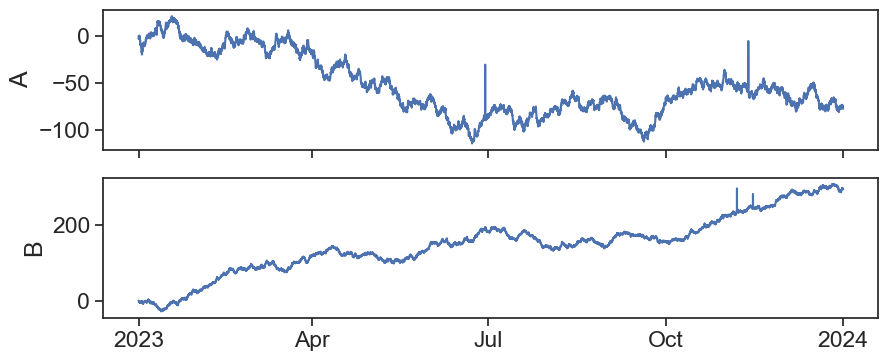
df2.dtypesA float64
B float64
dtype: objectdata_types = {'date': str , 'time':str}
# Read the CSV file with specified data types
df2 = pd.read_csv('cleaning2-.csv', delimiter=' ', dtype=data_types, na_values='-')
df2['datetime'] = pd.to_datetime(df2['date'] + ' ' + df2['time'], format='%d%m%Y %H:%M:%S')
df2.drop(columns=['date', 'time'], inplace=True)
df2.set_index('datetime', inplace=True)
df2| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| datetime | ||
| 2023-01-01 00:00:00 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| 2023-01-01 01:00:00 | -2.027536 | 0.011985 |
| 2023-01-01 02:00:00 | -2.690617 | -0.297928 |
| 2023-01-01 03:00:00 | -1.985990 | -0.309409 |
| 2023-01-01 04:00:00 | -2.290898 | -2.866663 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 2023-12-31 19:00:00 | -74.514645 | 293.868086 |
| 2023-12-31 20:00:00 | -74.738058 | 294.759346 |
| 2023-12-31 21:00:00 | -75.848425 | 294.076349 |
| 2023-12-31 22:00:00 | -77.272183 | 293.526461 |
| 2023-12-31 23:00:00 | -76.557400 | 293.353369 |
8760 rows × 2 columns
22.4 dataset 3
| # | |
|---|---|
| 0 | # data created by |
| 1 | # Yair Mau |
| 2 | # for time series data analysis |
| 3 | # |
| 4 | # time format: unix (s) |
| ... | ... |
| 370 | 6.651300774019661 1703635200.0 |
| 371 | 6.4151748349408715 1703721600.0 |
| 372 | 7.603140054178304 1703808000.0 |
| 373 | 8.668182044560869 1703894400.0 |
| 374 | 8.472767724946076 1703980800.0 |
375 rows × 1 columns
Again, let’s look at the actual .csv file.
| A time | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0.0 1672531200.0 |
| 1 | -0.03202661701444382 1672617600.0 |
| 2 | -0.5863508675173621 1672704000.0 |
| 3 | -1.5759721567247762 1672790400.0 |
| 4 | -2.7267995149281266 1672876800.0 |
| ... | ... |
| 360 | 6.651300774019661 1703635200.0 |
| 361 | 6.4151748349408715 1703721600.0 |
| 362 | 7.603140054178304 1703808000.0 |
| 363 | 8.668182044560869 1703894400.0 |
| 364 | 8.472767724946076 1703980800.0 |
365 rows × 1 columns
| A | time | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 1.672531e+09 |
| 1 | -0.032027 | 1.672618e+09 |
| 2 | -0.586351 | 1.672704e+09 |
| 3 | -1.575972 | 1.672790e+09 |
| 4 | -2.726800 | 1.672877e+09 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 360 | 6.651301 | 1.703635e+09 |
| 361 | 6.415175 | 1.703722e+09 |
| 362 | 7.603140 | 1.703808e+09 |
| 363 | 8.668182 | 1.703894e+09 |
| 364 | 8.472768 | 1.703981e+09 |
365 rows × 2 columns
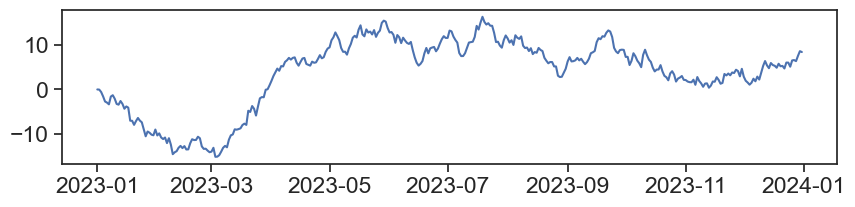
Time is in unix.
unix converter
| A | |
|---|---|
| time | |
| 2023-01-01 | 0.000000 |
| 2023-01-02 | -0.032027 |
| 2023-01-03 | -0.586351 |
| 2023-01-04 | -1.575972 |
| 2023-01-05 | -2.726800 |
| ... | ... |
| 2023-12-27 | 6.651301 |
| 2023-12-28 | 6.415175 |
| 2023-12-29 | 7.603140 |
| 2023-12-30 | 8.668182 |
| 2023-12-31 | 8.472768 |
365 rows × 1 columns
df3 = pd.read_csv('cleaning3.csv',
index_col='time', # set the column date as index
parse_dates=True, # turn to datetime format
comment='#',
delimiter=' ')
df3.index = pd.to_datetime(df3.index, unit='s')
df3| A | |
|---|---|
| time | |
| 2023-01-01 | 0.000000 |
| 2023-01-02 | -0.032027 |
| 2023-01-03 | -0.586351 |
| 2023-01-04 | -1.575972 |
| 2023-01-05 | -2.726800 |
| ... | ... |
| 2023-12-27 | 6.651301 |
| 2023-12-28 | 6.415175 |
| 2023-12-29 | 7.603140 |
| 2023-12-30 | 8.668182 |
| 2023-12-31 | 8.472768 |
365 rows × 1 columns