Introduction - lecture
- Sources
- How much water is there? Where?
- The water cycle
- Global water distribution
- Energy drives the hydrologic cycle
- Components of the water cycle
- References
Sources
Sources used:
(USGS, 2019) (USGS, 2019) (Margulis, 2017)
How much water is there? Where?

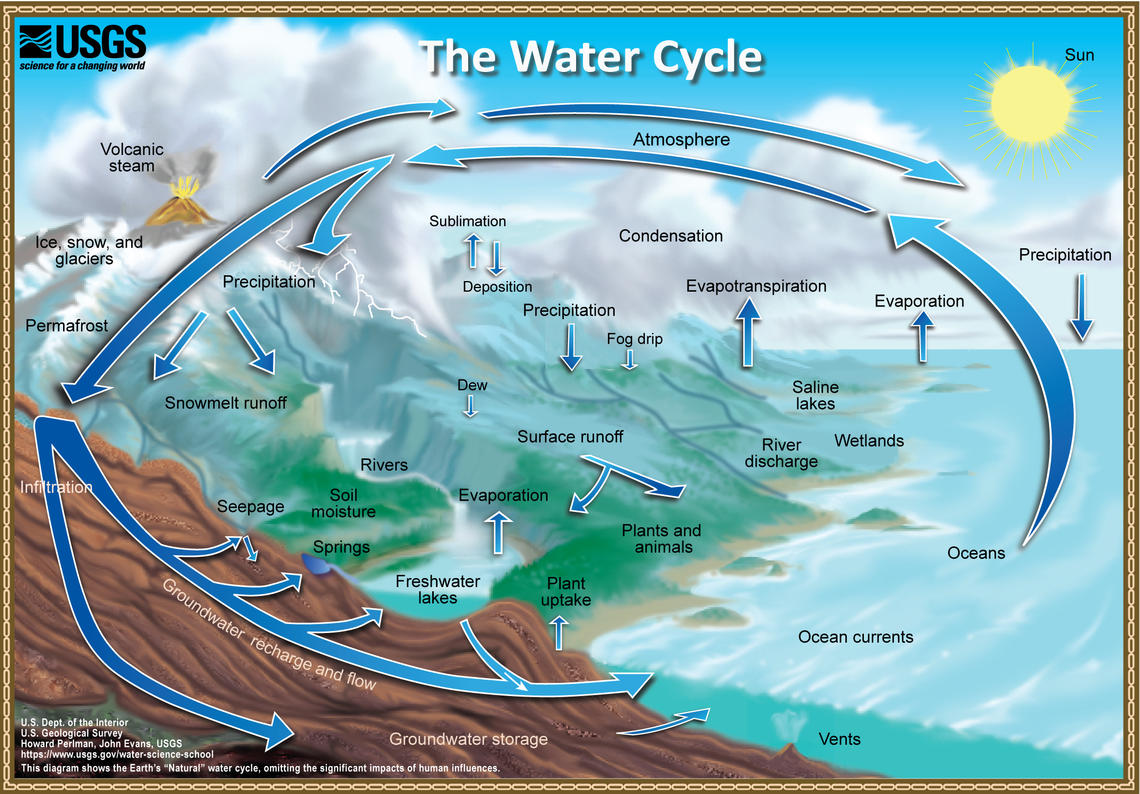
The water cycle
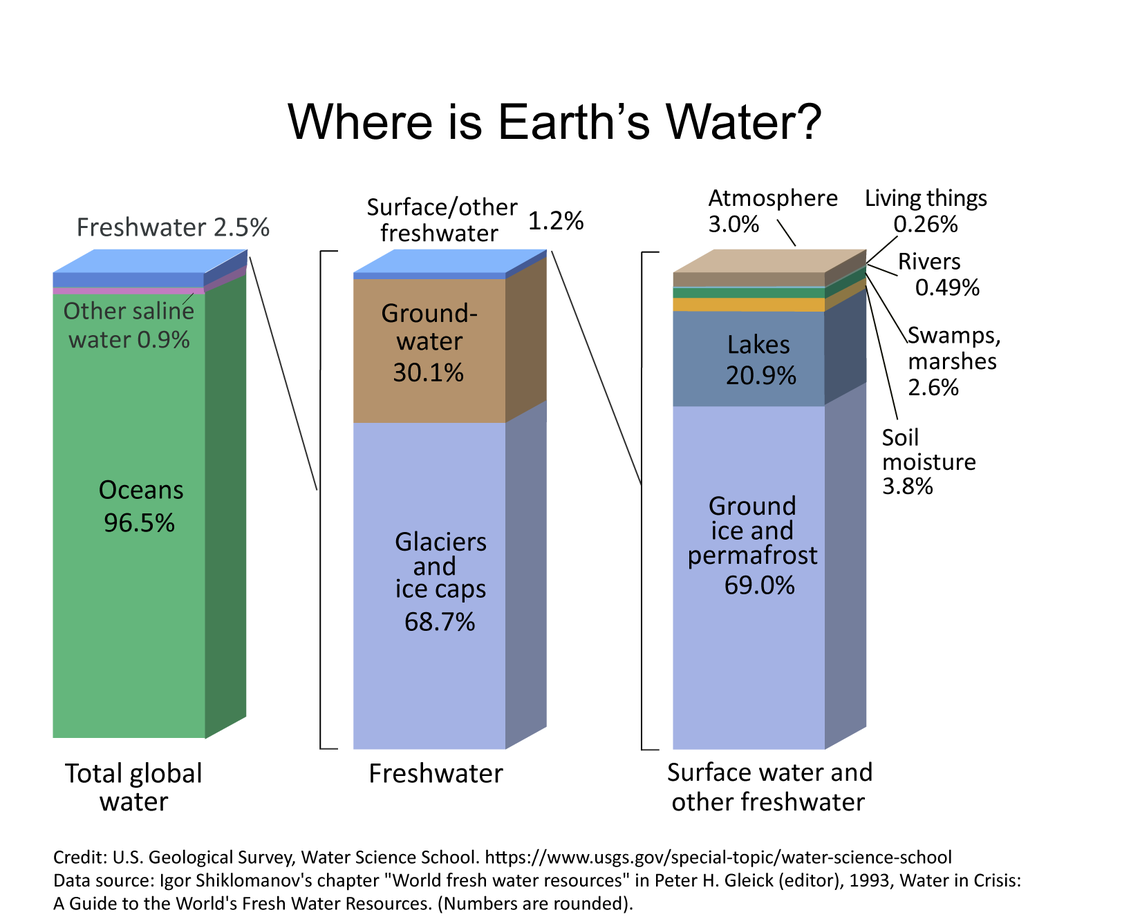
Global water distribution
| Water source | Volume (km$^3$) | % of freshwater | % of total water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oceans, Seas, & Bays | 1,338,000,000 | – | 96.54 |
| Ice caps, Glaciers, & Permanent Snow |
24,064,000 | 68.7 | 1.74 |
| Groundwater | 23,400,000 | – | 1.69 |
| $\quad$Fresh | 10,530,000 | 30.1 | 0.76 |
| $\quad$Saline | 12,870,000 | – | 0.93 |
| Soil Moisture | 16,500 | 0.05 | 0.001 |
| Ground Ice & Permafrost |
300,000 | 0.86 | 0.022 |
| Lakes | 176,400 | – | 0.013 |
| $\quad$Fresh | 91,000 | 0.26 | 0.007 |
| $\quad$Saline | 85,400 | – | 0.006 |
| Atmosphere | 12,900 | 0.04 | 0.001 |
| Swamp Water | 11,470 | 0.03 | 0.0008 |
| Rivers | 2,120 | 0.006 | 0.0002 |
| Biological Water | 1,120 | 0.003 | 0.0001 |
* (Percents are rounded, so will not add to 100)
https://www.usgs.gov/special-topic/water-science-school/science/fundamentals-water-cycle
Energy drives the hydrologic cycle
A key aspect of the hydrologic cycle is the fact that it is driven by energy inputs (primarily from the sun). At the global scale, the system is essentially closed with respect to water; negligible water is entering or leaving the system. In other words, there is no external forcing in terms of a water flux. Systems with no external forcing will generally eventually come to an equilibrium state. So what makes the hydrologic cycle so dynamic? The solar radiative energy input, which is external to the system, drives the hydrologic cycle. Averaged over the globe, 342 W m$^{-2}$ of solar radiative energy is being continuously input to the system at the top of the atmosphere. This energy input must be dissipated, and this is done, to a large extent, via the hydrologic cycle. Due to this fact, the study of hydrology is not isolated to the study of water storage and movement, but also must often include study of energy storage and movements.
Margulis, 2017, “Introduction to Hydrology”
Components of the water cycle
Water storage in oceans
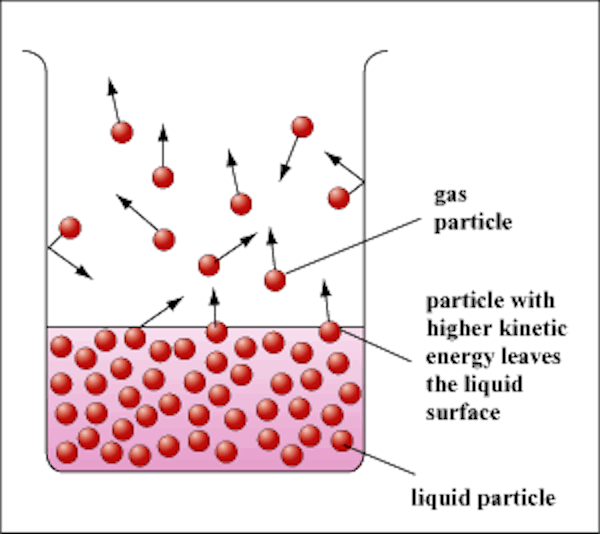
Evaporation / Sublimation
Evaporation $\longrightarrow$ cooling

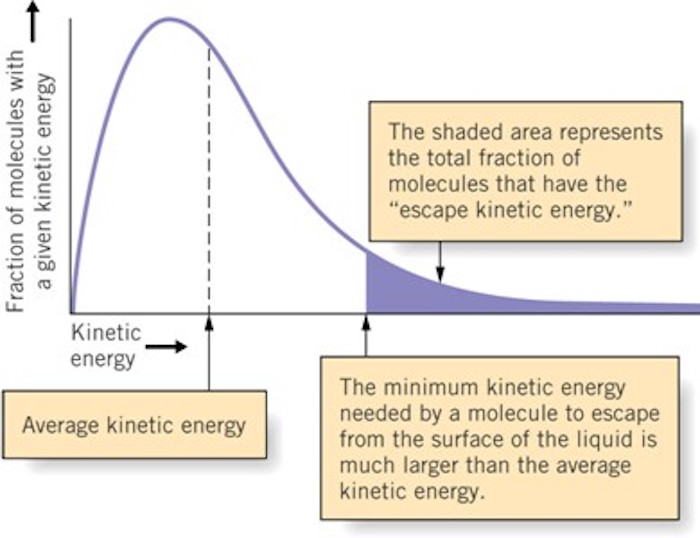
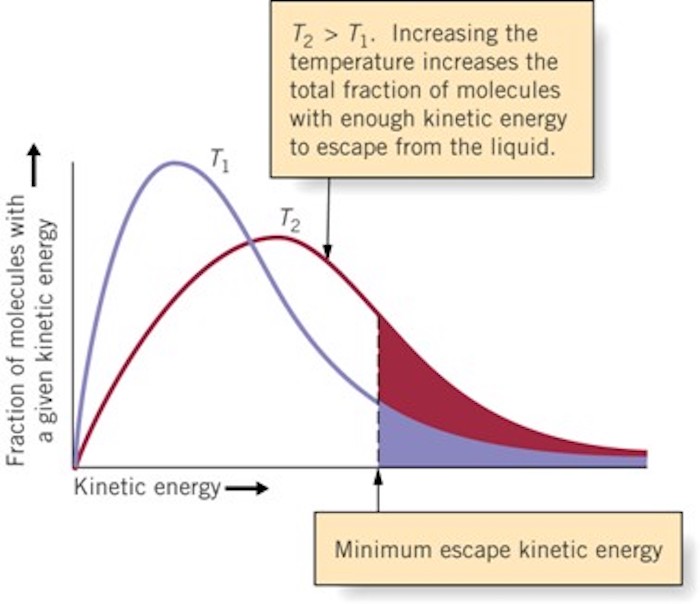
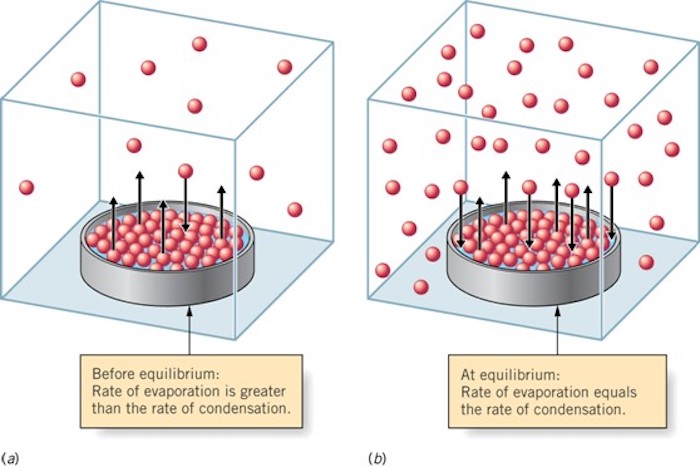
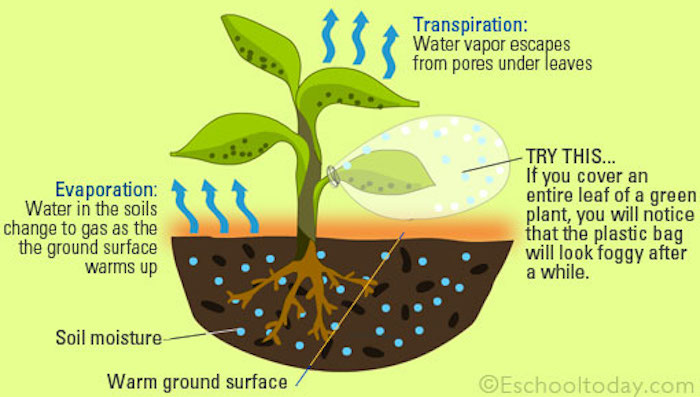
Evapotranspiration
Water storage in the atmosphere
Cumulonimbus cloud over Africa
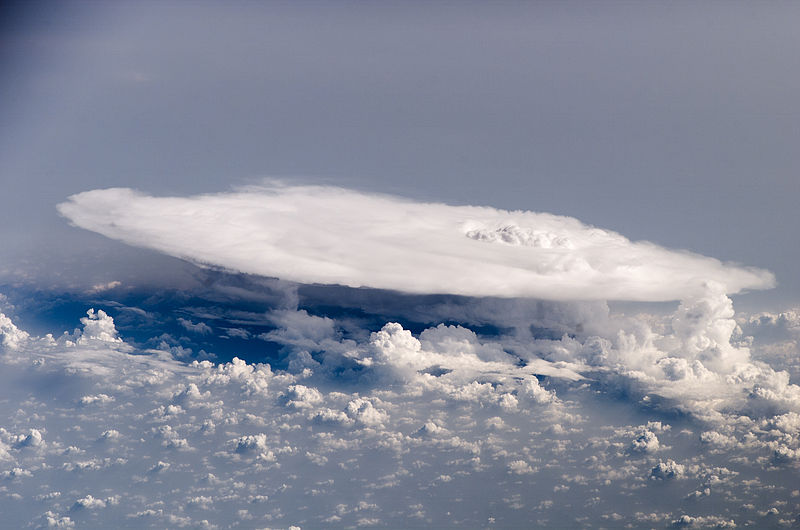

Picture of cumulonimbus taken from the International Space Station, over western Africa near the Senegal-Mali border.
If all of the water in the atmosphere rained down at once, it would only cover the globe to a depth of 2.5 centimeters.
Try to calculate this yourself, and click on the button below to check how to do it.
Condensation
Precipitation

| Intensity (cm/h) | Median diameter (mm) | Velocity of fall (m/s) | Drops s$^{-1}$ m$^{-2}$ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fog | 0.013 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 67,425,000 |
| Mist | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.21 | 27,000 |
| Drizzle | 0.025 | 0.96 | 4.1 | 151 |
| Light rain | 0.10 | 1.24 | 4.8 | 280 |
| Moderate rain | 0.38 | 1.60 | 5.7 | 495 |
| Heavy rain | 1.52 | 2.05 | 6.7 | 495 |
| Excessive rain | 4.06 | 2.40 | 7.3 | 818 |
| Cloudburst | 10.2 | 2.85 | 7.9 | 1,220 |
Source: usgs.gov
Water storage in ice and snow
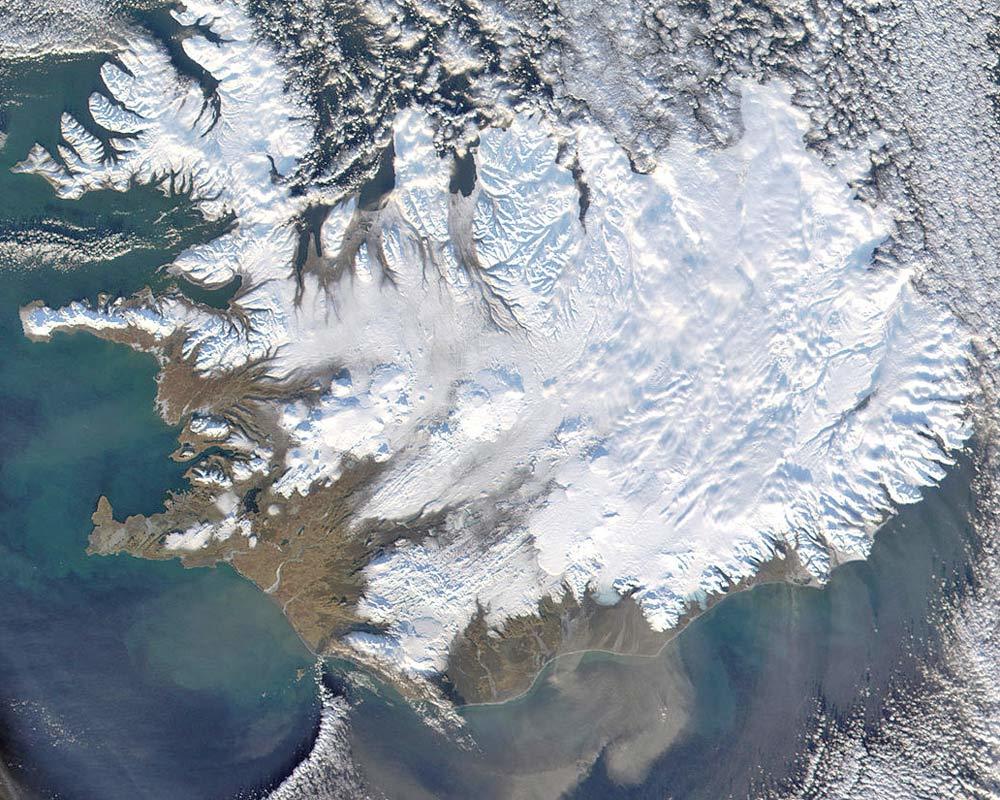

Snowmelt runoff to streams
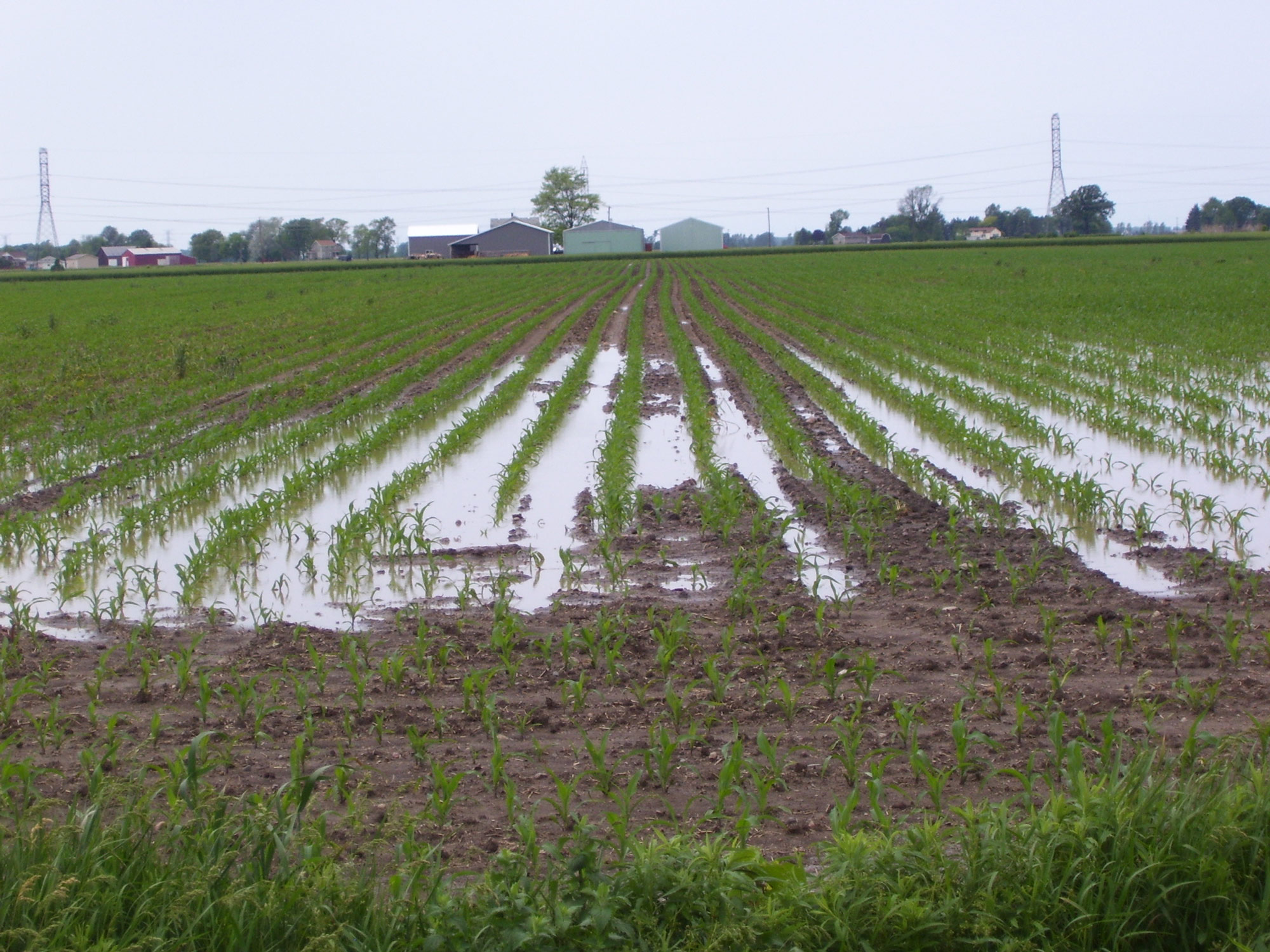
Surface runoff
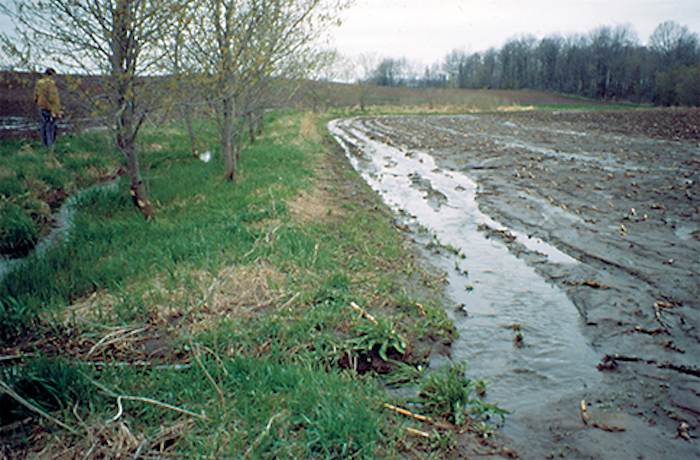
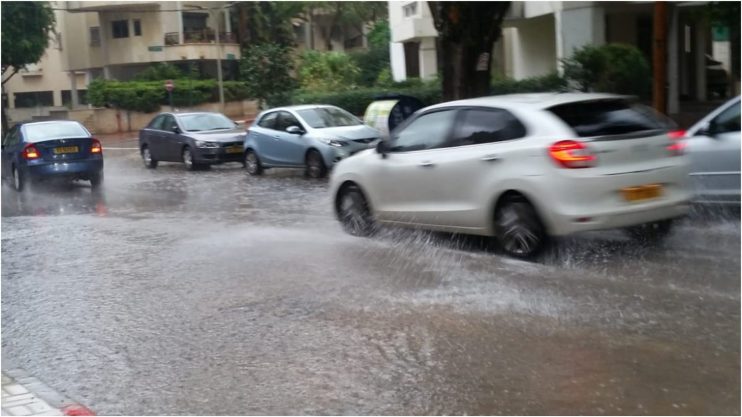


Streamflow
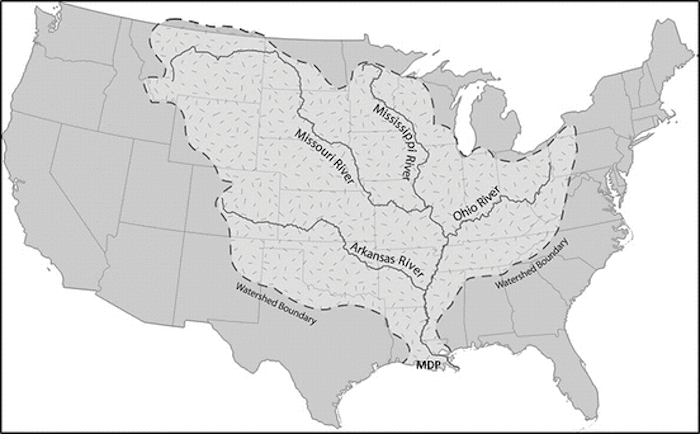
The Mississippi river basin is very large
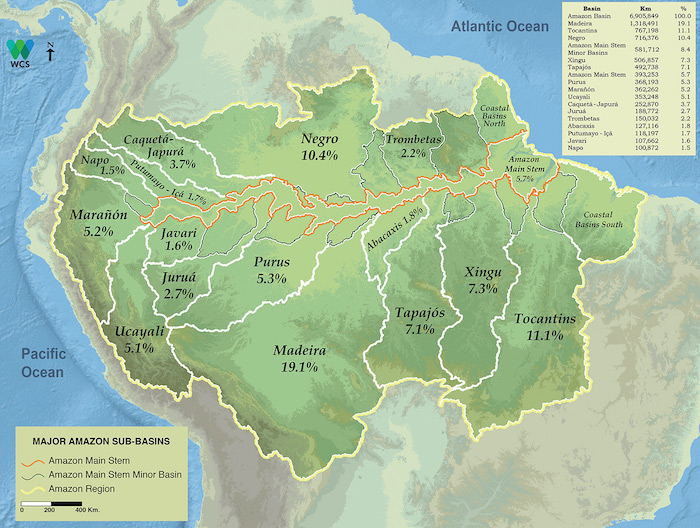
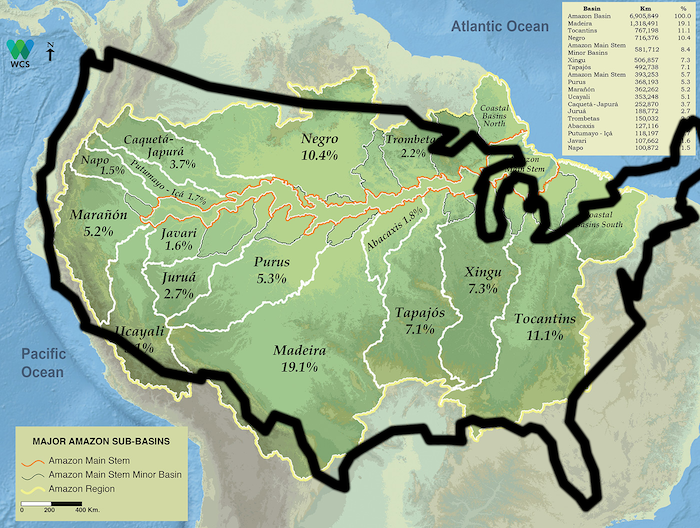
The Amazon river basin is Huge
Lakes and rivers
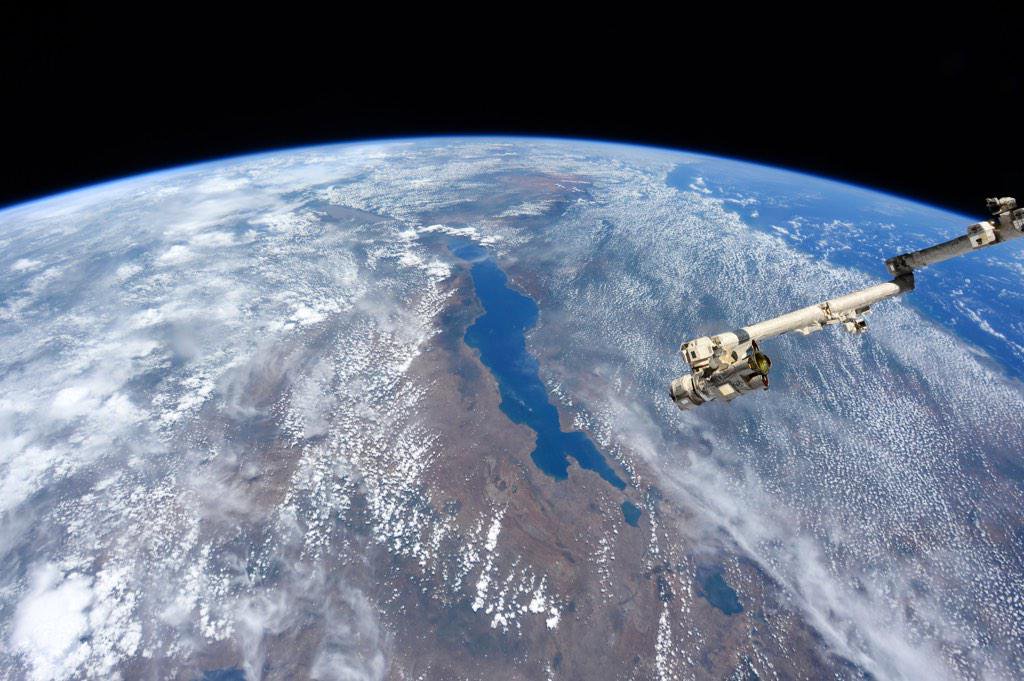
Lake Malawi


Infiltration

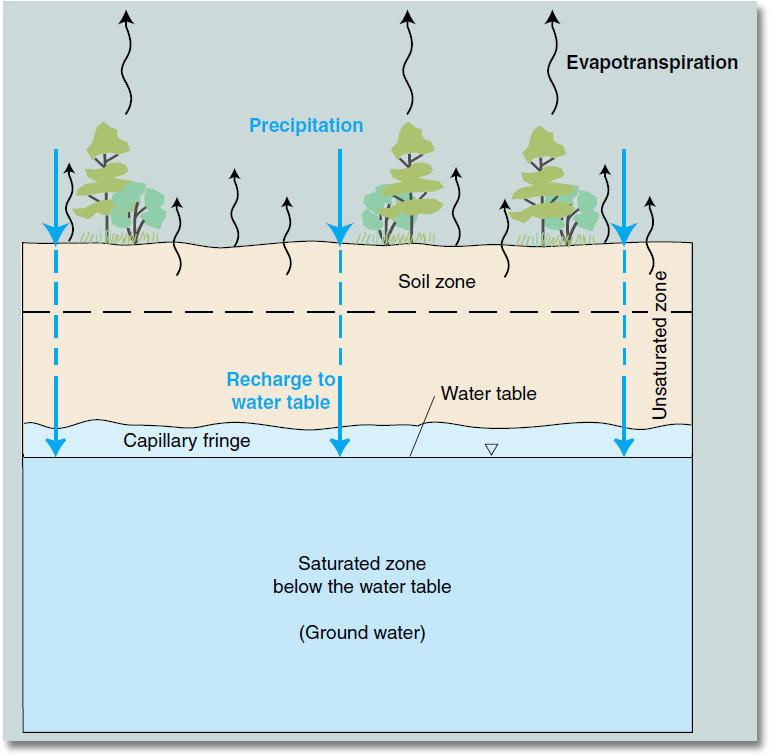
Groundwater storage
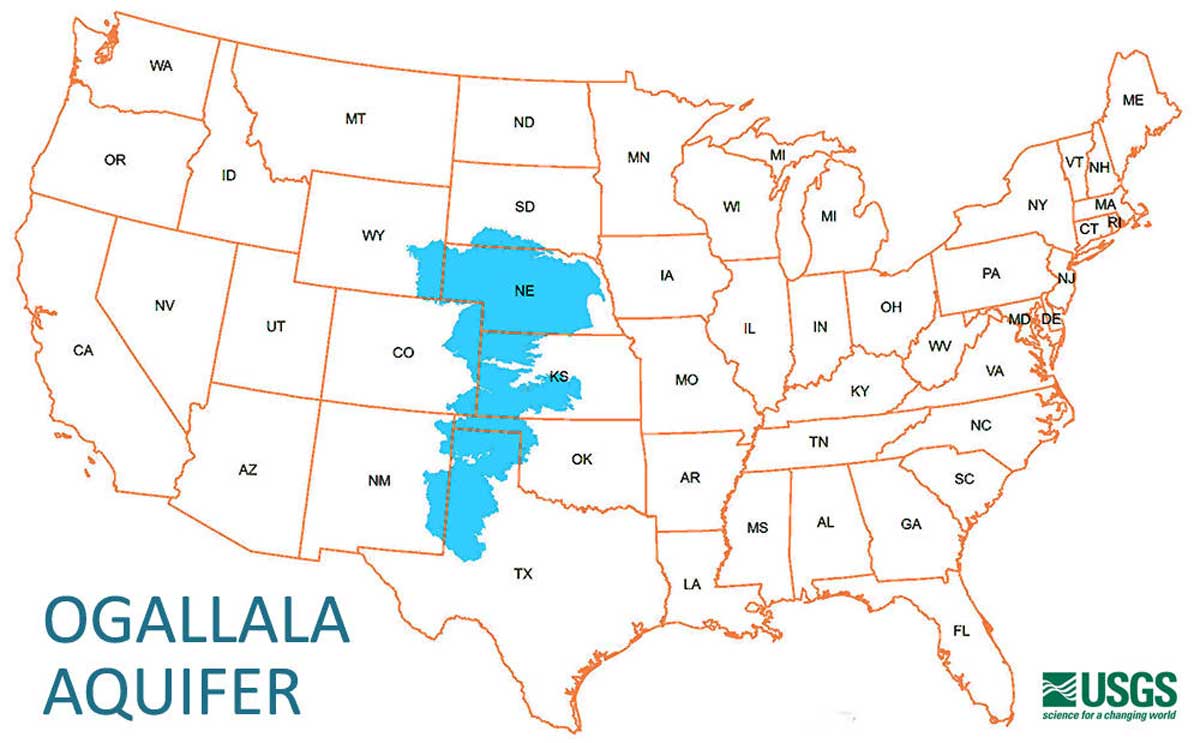
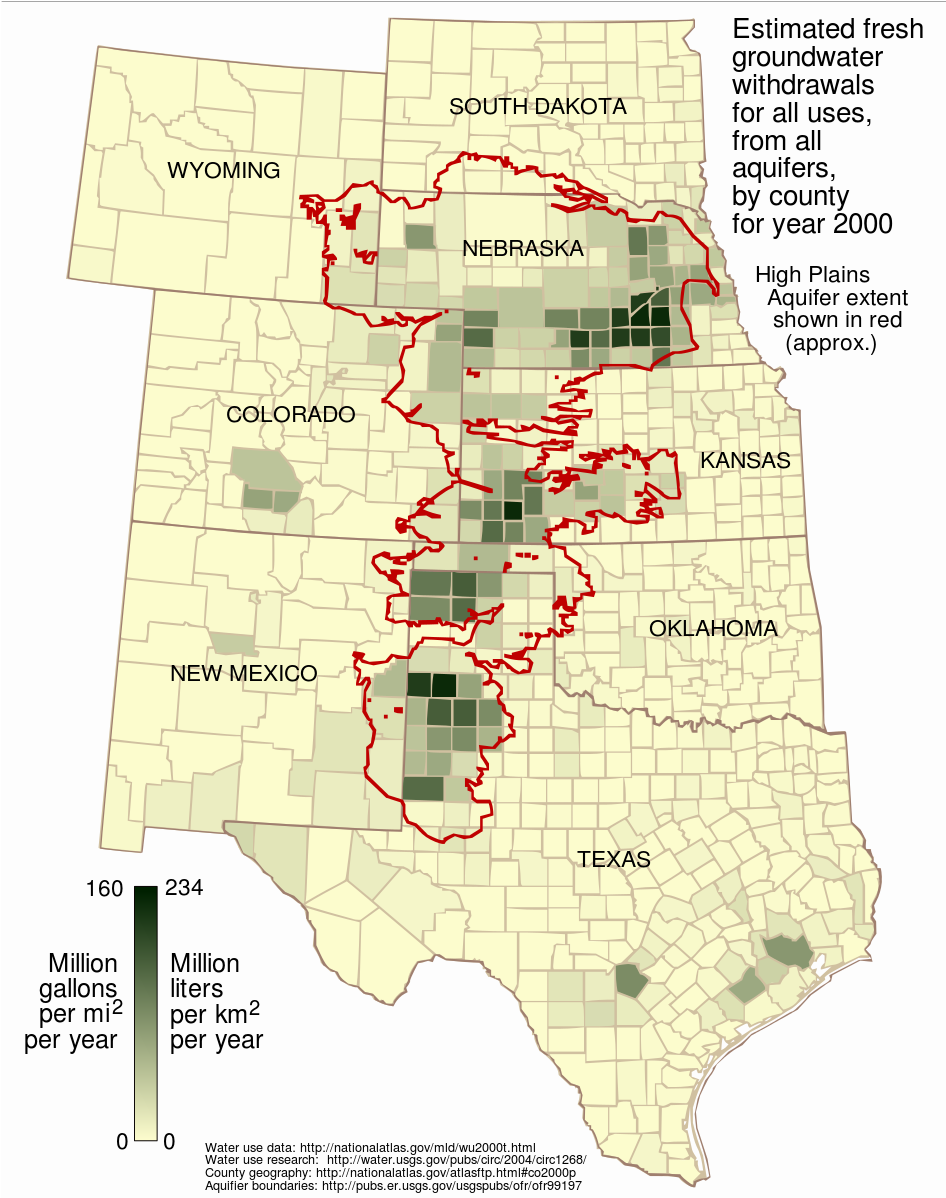
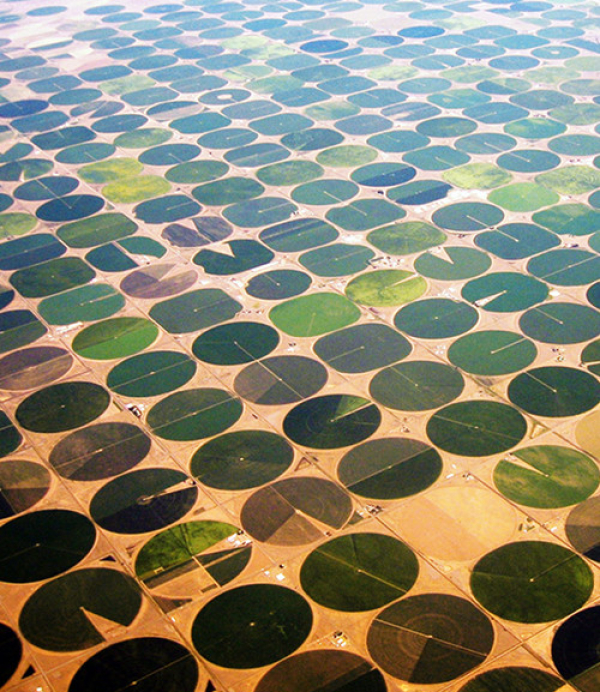
Center Pivot irrigation in Nebraska taps the Ogallala Aquifer.

Groundwater flow and discharge
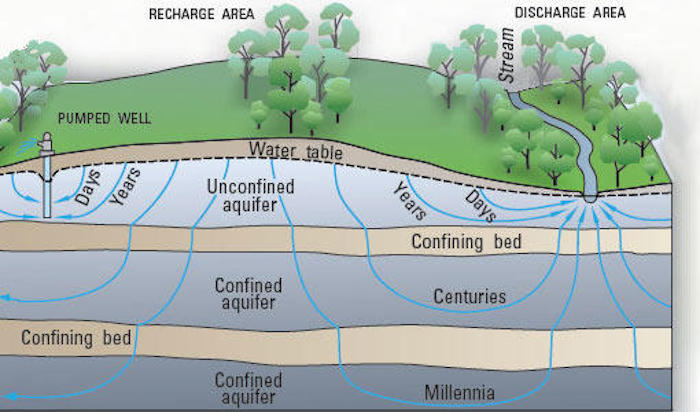
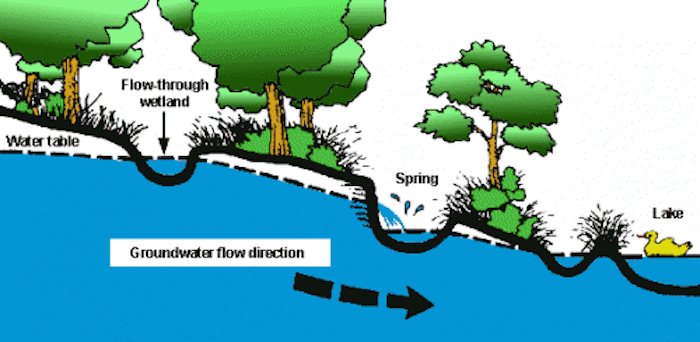
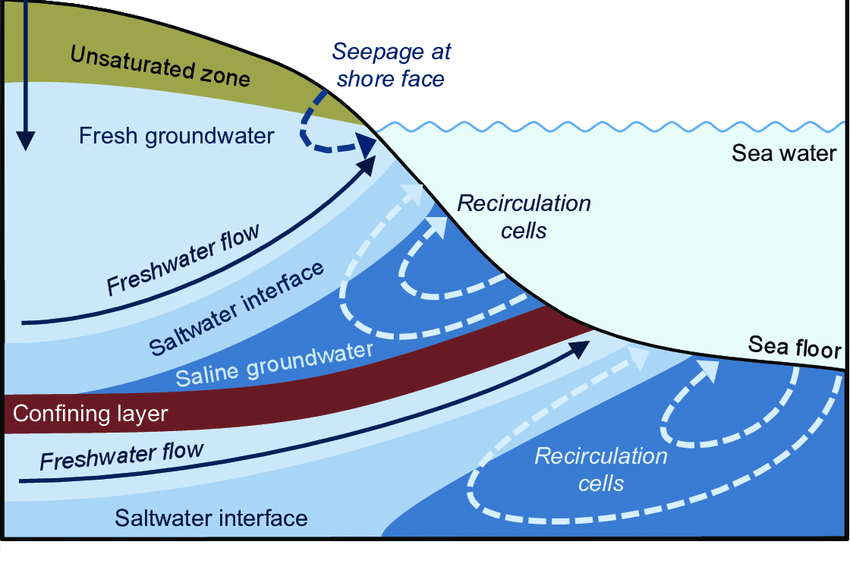
Spring
Ein Gedi


References
- USGS, 2019. How Much Water is There on Earth?
- USGS, 2019. Water Science School.
- Margulis, S., 2017. Introduction to Hydrology. eBook.